Fixed Income
Responding to equity-like volatility in frontier bonds

Fixed Income

In 2022, we saw an increasing breakdown of correlations across the investment landscape. The demise of the classic 60/40 portfolio structure has been well publicised, and in the fixed income universe, the usual negative correlation between interest rates and spreads switched to a positive relationship.
Not to miss out on the ‘all-change’ trend, frontier bond markets, which come with their own uniquely complex dynamics at the best of times, also delivered a correlation phenomenon last year.
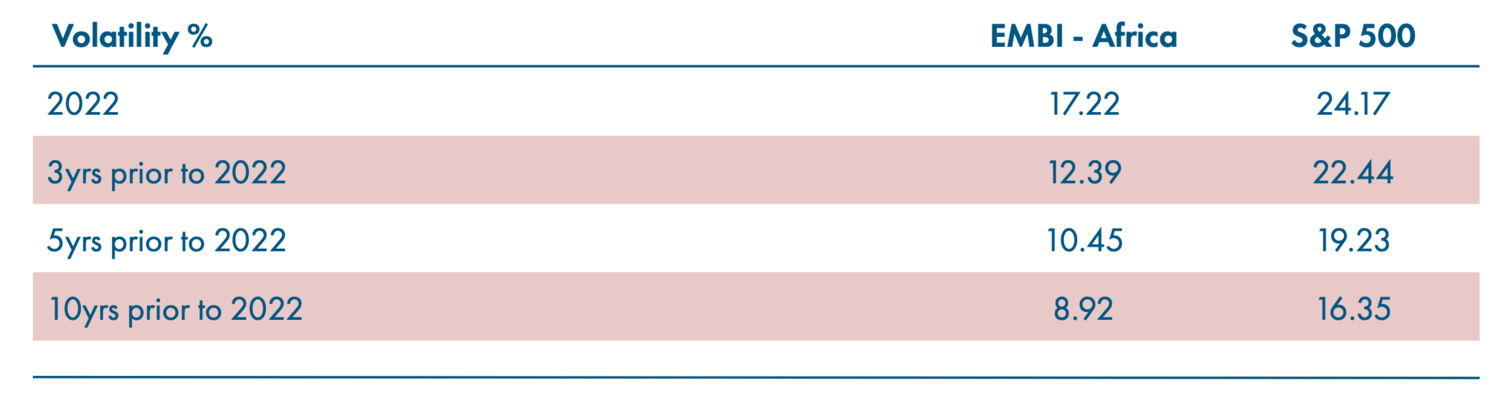
While frontier markets sit at the risker end of the EM fixed income universe, their volatility profile is typically well below that of equities. But last year, we saw the volatility of African hard currency (HC) sovereign bonds1 (a proxy for frontier markets) almost double – rising from a 10-year annualised average2 of 8.9% to 17.2% for 2022 (annualised). This puts them on par with the average 10-year annualised volatility of the S&P 500 Index, which clocks in at 16.4%2 and displayed a more modest jump to 24.2% in 2022 (Table 1).
Source: Bloomberg, February 2023. EMBI - Africa refers to the African sub-index component of the J.P. Morgan Emerging Market Bond Index, which is used as a proxy for hard currency frontier market bonds.
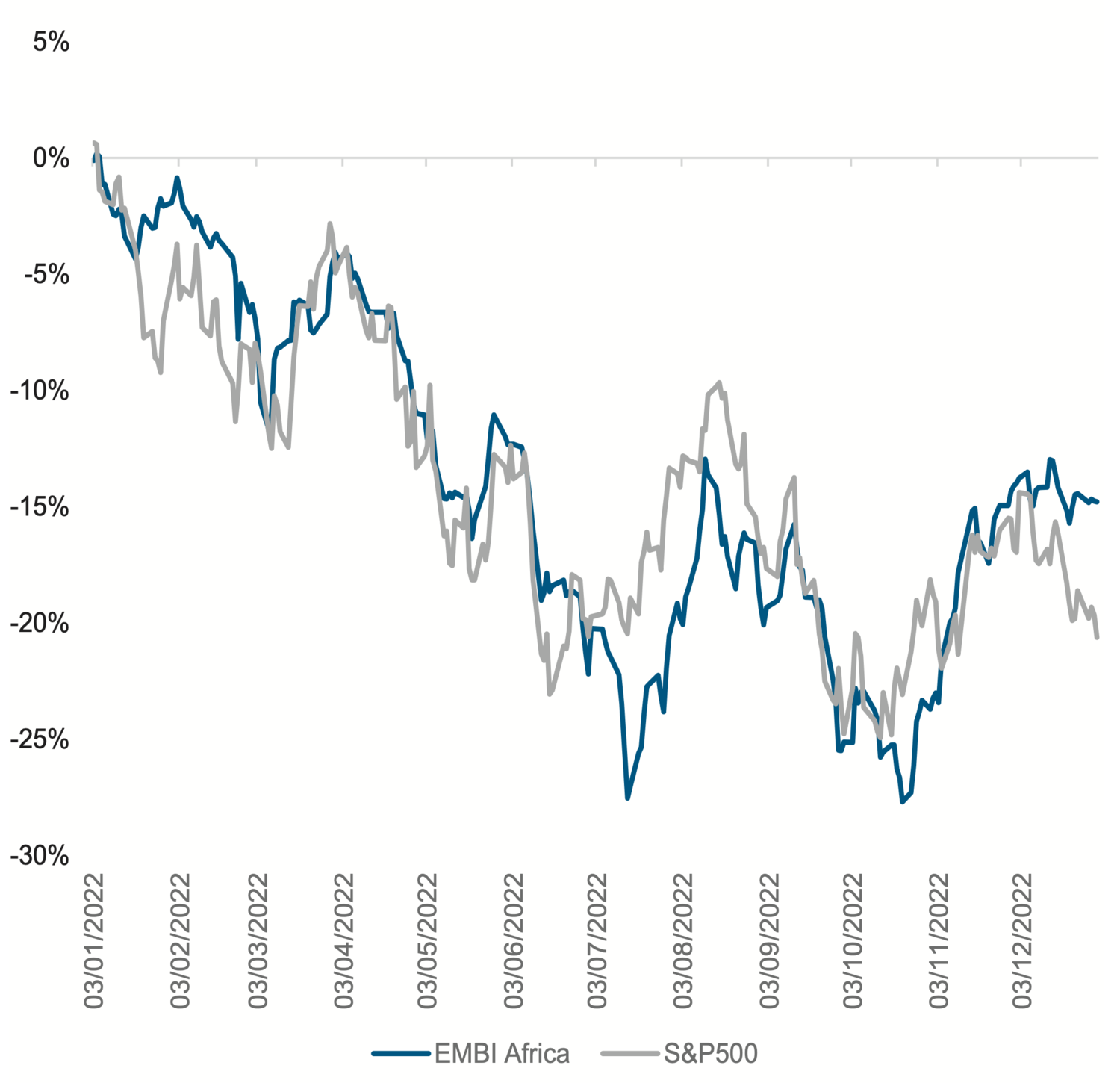
Seasoned investors will be familiar with the adage that changes in the macro-economic environment can cause shifts in the underlying volatility and correlations of asset classes. Shifting interest rate policy in the US, combined with the heightened geopolitics that we saw last year, provide a vivid example of this theory in action for frontier markets as they traded almost in unison with the S&P 500 (Chart 1).
While there’s seemingly no obvious comparison between US equities and HC frontier bonds, both markets are sensitive to growth and, even more importantly, to changing financial conditions.
Frontier economies typically rely on foreign capital flows to fund their current account and government deficits, as they lack deep domestic capital markets and FDI flows.
Foreign capital flows are subject to global financial conditions and the macro risk environment, which was extremely weak last year and has been oscillating since the start of the pandemic in early 2020.
Given the uncertainty of frontier economies to fund themselves in a timely manner, their debt-carrying capacity is lower and tight liquidity conditions can quickly turn into solvency issues.
Source: Bloomberg, February 2023. EMBI - Africa refers to the African sub-index component of the J.P. Morgan Emerging Market Bond Index, which is used as a proxy for hard currency frontier market bonds.
We saw this play out over the last couple of years in some frontier economies, such as Sri Lanka, Ghana and Zambia. Even Angola, which is one of the biggest beneficiaries of elevated oil prices, experienced notable bond price volatility last year with the tightening of financial conditions.
Angola generates over 90% of its foreign earnings and over 60% of its fiscal revenues from hydrocarbons. Hence, the economy saw a significant improvement to its external accounts in 2022, in addition to registering a budget surplus and real GDP growth of approximately 3%. However, with the tightening financial conditions, the volatility of its USD-denominated bonds jumped to 22% in the belly of the curve and around 28% in the long end, versus 10% and 11% in 2021, respectively.
While the increased correlation between the frontier markets and the S&P in 2022 is interesting at an anecdotal level, it also provides a refresher on the nature of frontiers – they are complex and undulating markets that can deliver big highs and big lows. From mid-October 2022 to January 2023, HC frontier bonds registered a staggering 21% rally3 highlighting the potential upside of embracing the investment complexities.
Having had such a strong run, we were mindful of potential downside in the frontier space and have been realising gains on our exposures to crystalise the winter performance.
Looking across the EM debt landscape, we have been investing in short-dated investment grade bonds with attractive all-in yields, and select better-quality high yield bonds, as they are less sensitive to the ongoing transition of inflation risks to growth concerns.
As for the frontier markets, it is as important to avoid weaker credits as much as it is to be invested in the right names. This cohort requires quality fundamental analysis paired with a nimble and flexible active management to harness its alpha-generation potential. With a weighting of over 12% in the EMBI benchmark, this sub-sector is not something to ignore, but rather invested in with an understanding of its equity-like properties.
1. Represented by the J.P. Morgan Emerging Market Bond Index - Africa sub-index component
2. 10-year average measured from 2012 to 2021
3. Measured using the J.P. Morgan Emerging Market Bond Index - Africa sub-index component
Continue to